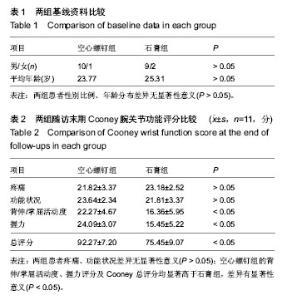
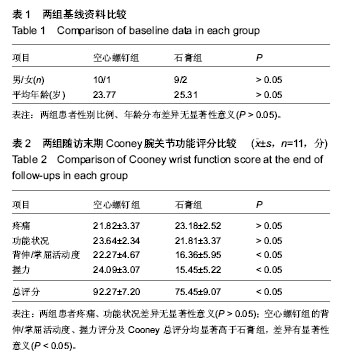
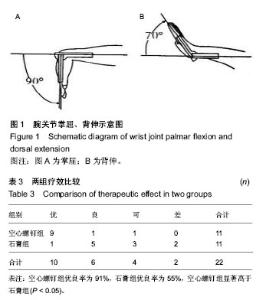
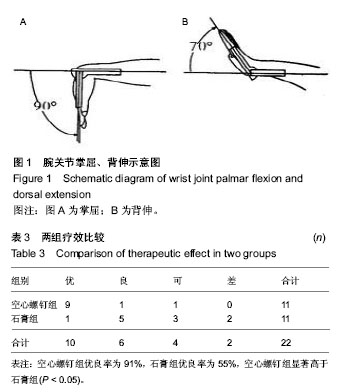
[2] Miri D,Vuceti C,Senohradski K,et al.Incidence and severity of degenerative changes in the wrist in pseudoarthrosis of the scaphoid bone. Srp Arh Celok Lek. 2001;129(3-4): 61-65.
[3] Ruby LK,Stinson J,Belsky MR.The natural history of scaphoid nonunion.A review of fifty-five cases.J Bone joint Surg Am. 1985;67(3):428-432.
[4] 胥少汀,葛宝丰,徐印坎,主编.实用骨科学[M].4版.北京:人民军医出版社,2012:129.
[5] Egol KA, Koval KJ, Zuckerman JD.骨折手册[M].蒋协远主译. 4版.北京:人民军医出版社,2012:315.
[6] Herbert TJ,Fisher WE.Management of the fractured scaphoid using a new bone screw.J Bone Joint Surg(Br). 1984; 66(1):114-123.
[7] Russe O.Fracture of the carpal navicular.J Bone Joint Surg(Am).1960;42:759-768.
[8] Cooney WP. Scaphoid fracture:current treatment and techniques. Instr Course Lect.2003;52:197-208.
[9] 坎贝尔.骨科手术学[M].12版.王岩,毕郑刚主译.北京:人民军医出版社,2013:3155.
[10] 吴在德,吴肇汉,主编.外科学(第七版)[M].北京:人民卫生出版社, 2008:731-737.
[11] Thomas PR,Richard EB,Christopher GM,主编.骨折治疗的AO原则(第二版)[M].危杰,刘瑶,吴新宝,等主译.上海:上海科学技术出版社,2010:3-7.
[12] 刘斌,张立岩,王济纬,等.空心拉力螺钉治疗腕舟状骨骨折疗效分析[J].中国骨伤,2010,23(3),227-228.
[13] 齐涛,陈光,张义.应用ASIF空心钉治疗腕舟骨骨折22例[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2005,13(4):318-319.
[14] 顾文奇,梅国华,柴益民.无头加压空心螺钉治疗舟状骨骨折的早期疗效[J].中国修复重建外科杂志,2011,25(6):767-768.
[15] 贺喜顺,杨惠林,谭相齐,等.Bold螺钉治疗腕舟骨骨折[J].临床骨科杂志,2008,11(2):154-156.
[16] 何正华,徐明,余鹏,等.AO空心钉治疗腕舟骨骨折[J].实用医学杂志,2008,24(2):261-262.
[17] 陈振兵,洪光祥,王发斌,等.加压螺钉治疗舟骨骨折的临床疗效[J].中华手外科杂志,2005,21(1):28-30.
[18] Hausmann JT,Maur W,Unger E,et al.Interfragmentary compression forces of scaphoid screws in a sawbone cylinder model. Injury. 2007;38(7):763-768.
[19] Trousdle RT,Amadiao PC,Cooney WP,et al.Radio-ulner dissociation.A review of twenty cases. J Bone joint Surg(Am). 1992;74:1486-1497.
[20] Hausmann JT, Maur W,Unger E, et al.Interfragmentary compression forces of scaphoid screws in a sawbone cylinder model. Injury. 2007;38(7):763-768.
[21] 王虎,牛银立,胡芳,等.腕舟骨骨折夹角与x线形态的对照分析[J].实用放射学杂志,2008,17(2):130-131.
[22] 松庆,唐焕章.带血管筋膜蒂桡骨茎突骨膜骨瓣修复舟状骨骨不连[J].中国修复重建外科杂志,2005,19(4):269-269.
[23] 董军.可吸收螺钉治疗新鲜不稳定型腕舟状骨骨折16例疗效观察[J].中国保健营养(中旬刊),2012,(12):320-321.
[24] 李庆泰.必须重视手部骨折的治疗[J].中国实用手外科杂志,2000, 14(1):3-5.
[25] 吴在德,吴肇汉,主编.外科学(第七版)[M].北京:人民卫生出版社, 2008:731-737.
[26] Rtledi TP,Buckley RE,Moran CG,主编.危杰,刘瑶,吴新宝,等主译.骨折治疗的AO原则(第二版)[M].上海:上海科学技术出版社, 2010:3-7.
[27] 乔栓杰,逢育,连坡,等,加压螺钉内固定治疗腕舟状骨骨折[J].中国骨伤,2004,17(9):567-568
[28] 赵敏,龚国玲,袁太珍.可吸收螺钉治疗不稳定型腕舟骨骨折效果观察[J].海南医学,2011,22(16):84-85.
[29] 王澍寰,主编.手外科学(第三版)[M].北京:人民卫生出版社,2011: 191-199,242-249,298-306.
[30] 路来金,刘志刚,中村蓼吾,等.腕舟骨骨折的临床诊断和治疗[J].中华手外科杂志,1998,14(3):144-146.
[31] Herbert TJ.Management ofthe fraenz'ed scaphoid using anew bone screw.Bone Jo int Surg(Am).1984: 66-114.
[32] Trumble TE,Gilbert M,Murray LW,et al.Displaced scaphoid fractures treated with open reduction and internal fixation with a cannulated screw.J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2000;82(5):633-641.
[33] 超斌,陈振兵,王忠仁,等.Herber t螺钉微创治疗腕舟骨骨折[J].实用骨科杂志,2010,16(2):90-92.
[34] Filan SL,Herbert TJ.Herbert screw fixation of scaphoid fractures.J Bone Joint Surg Br.1996;78:519-529.